In the biogas production process, what is HRT?
Reading time: approximately 4m28s
Discover the meaning and importance of Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT) in anaerobic processes. Learn how to calculate, size reactors, and optimize biogas production. Explore the relationship between HRT and energy efficiency.
What is HRT?
Understanding the HRT Parameter in Anaerobic Processes: A Comprehensive Perspective
What is HRT?
The Time of Hydraulic Retention (HRT) is a crucial parameter in anaerobic processes, especially in biodigestion systems. It represents the average time that organic matter remains inside the reactor, being exposed to ideal conditions for degradation by anaerobic microorganisms, resulting in biogas production.
What is the formula to calculate HRT?
HRT = V / Q
Where:
-
- HRT is the Time of Hydraulic Retention (in days)
- V is the volume of the reactor (in cubic meters, m³)
- Q is the inflow rate of organic substrate (in cubic meters per day, m³/day)
This formula simply divides the reactor volume by the inflow rate of organic substrate to determine how long, on average, the substrate remains inside the reactor before being discharged. This time is crucial for the effectiveness of the anaerobic process, as it directly affects the amount of substrate available for microorganisms and, therefore, biogas production.
What is the importance of HRT in biogas projects?
HRT is vital for the anaerobic process for several reasons:
-
- Degradability Efficiency: Adequate HRT ensures that organic matter is efficiently decomposed by microorganisms, maximizing biogas production and minimizing the amount of undigested organic waste.
- Process Stability: A well-adjusted HRT contributes to the stability of the anaerobic process, reducing the risk of operational failures such as reactor acidification or foam formation.
- Reactor Sizing: HRT directly influences the sizing of anaerobic reactors. A longer HRT may require larger reactors to accommodate the same organic load, while a shorter HRT may allow for smaller reactors.
What is the impact on reactor operation & maintenance (O&M)?
HRT significantly affects the operation and efficiency of organic matter biodegradation, as well as biogas production. Below are some sensitive points regarding this parameter:
-
- Biodegradation Efficiency: A very short HRT can result in incomplete organic matter degradation, reducing biogas production and increasing the need for additional effluent treatment.
- Biogas Production: An optimized HRT increases biogas production, which can be used as a renewable energy source.
- Maintenance: HRT influences the frequency and intensity of maintenance activities, such as sediment removal and reactor cleaning.
What is the importance of Mathematical Modeling, Computational Simulation, and Experimental Tests in identifying and adjusting the appropriate HRT for each reactor??
Mathematical modeling, computational simulation, and experimental tests play a fundamental role in identifying the ideal HRT for a specific anaerobic system. These tools allow engineers and operators to test different HRT scenarios, optimizing the process and finding the best cost-benefit ratio between reactor design and its operation/maintenance. By combining experimental data with computational simulations, it is possible to accurately predict the system's performance under different operating conditions, ensuring efficient and economical operation of the anaerobic reactor.
In summary, HRT is a critical parameter in anaerobic processes, and its optimization is essential to maximize biogas production, ensure the efficiency of organic matter degradation, and minimize operating costs. The use of modeling and simulation tools is essential to achieve these goals, allowing for a more precise and economical approach to the design and operation of anaerobic reactors.
Consulted Bibliographic References
- CHERNICHARO, CA de L. et al. Principles of biological treatment of wastewater: anaerobic reactors. Belo Horizonte: Department of Sanitary and Environmental Engineering, Federal University of Minas Gerais, v. 5, p. 379, 2007.
- KUNZ, Airton; STEINMETZ, Ricardo Luis Radis; DO AMARAL, André Cestonaro. Fundamentals of anaerobic digestion, biogas purification, use and treatment of digestate. 2nd ed. Concórdia: Sbera: Embrapa Suínos e Aves, 2022. Pages: 214 p. ISBN: 978-65-88155-02-8
- LIMA, H. Q. Evaluation of Hashimoto and AMS-III.D models for methane production with swine manure. 2011. 99 f. Dissertation (Master's degree) - Center for Engineering, Modeling and Applied Social Sciences, Federal University of ABC, Santo André - SP, 2011.
What do you think about this agenda? Feel free, contribute, and leave your comment.
See you soon!
Series of posts "Knowledge Nuggets"
What are granules?
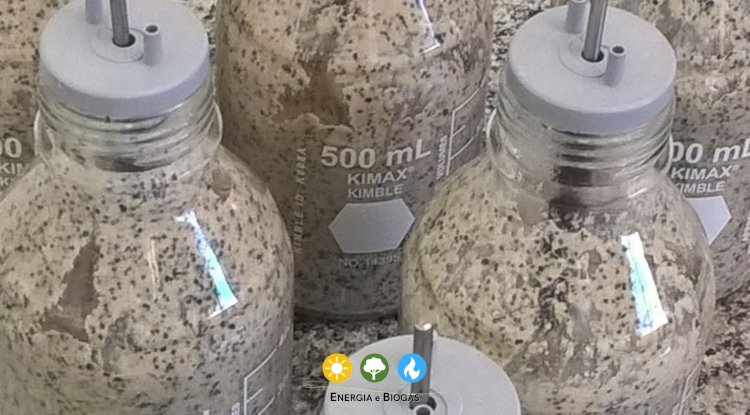
About anaerobic processes, under certain conditions, there is the formation of structures consisting of anaerobic microorganisms, the anaerobic granules.
These structures (clusters of different microorganisms) enable more efficient nutrient transfer and promote the survival of the microbial community.
These densely packed clusters of microorganisms contribute to the acceleration of the anaerobic digestion process, especially in UASB reactor sludges.
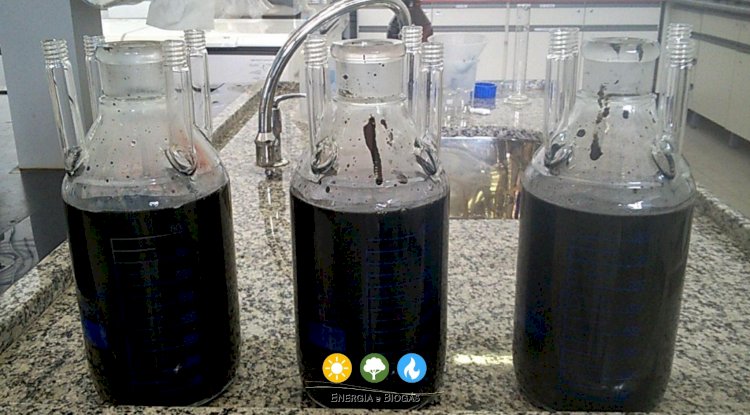

The anaerobic granules are very small spheres and have a vast community of living beings. They act on the decomposition of organic matter and enable nutrient recycling.

Following the concept of "small pearls with condensed content", the Energy and Biogas Portal publishes a series of posts "Knowledge Nuggets" - small posts to contribute to the dissemination of information about the biogas production process.
Always follow our specific content about the science behind the anaerobic process and biogas production.
New posts "Knowledge Nuggets" coming soon.
See you soon!
To explore other concepts, access our Glossary.
Also access Biogas in Brazil.
Thank you and happy reading!
Check out other articles from the Energy and Biogas Portal, access:
- Biogas, Biomethane
- Anaerobic Digestion
- Biodigester - Anaerobic reactor
- Substrates - the raw material for biogas production
- What is Sulfetogenesis?
Copyright © 2018 - 2024 All rights reserved - Energy and Biogas Portal®.











NOTICE! The space for comments is intended for a healthy debate of ideas. Posts containing inappropriate expressions or personal attacks on the publication team, another user or any identified group or individual will not be accepted. If this occurs, we reserve the right to delete the comment to maintain a respectful environment for discussion.